Kuwait offers various residency visa options for foreigners wishing to live, work, or join family members in the country.
Whether you're relocating for employment, starting a business, or reuniting with loved ones, understanding the residency system is essential.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Kuwait’s residency visa categories, application procedures, eligibility requirements, and legal obligations, helping you navigate the process with confidence and ease. To begin your journey, it's important to apply for Kuwait Visa through the official channels and ensure all documentation is accurate and up to date.

Types of Residency Visas in Kuwait
Each visa type has specific requirements and conditions designed to regulate the stay of foreign nationals. Below is a concise overview of the main residency visa types in Kuwait.
|
Visa Type |
Description |
|
Work Residency Visa (Article 18) |
For foreign workers sponsored by a Kuwaiti employer. Requires a job offer and work permit. Valid and renewable as long as employment continues. |
|
Family Residency Visa (Article 22) |
For spouses, children, or parents of legal residents. Sponsors must meet minimum salary. Dependents cannot work unless they transfer to a work visa. |
|
Student Residency Visa |
Issued to foreign students enrolled in approved institutions. Requires admission proof and financial support. Valid for the study period and renewable. |
|
Investor/Business Visa |
For foreign investors or entrepreneurs. Requires capital investment and government approval. Often self-sponsored and supports long-term stay. |
|
Domestic Worker Visa (Article 20) |
For household staff (maids, drivers, nannies). Sponsored by the employer, who is responsible for renewal and legal status. Not transferable to other sectors. |
|
Temporary Residency Visa |
For short-term stays (e.g., training, transition). Valid for up to 3 months, non-renewable, and used for temporary purposes only. |
Requirements for Kuwait Residency Visas
To obtain a residency visa in Kuwait, applicants must fulfill specific documentation and procedural requirements based on the visa category.
Providing the correct and complete documents is essential for timely approval and legal compliance. Below is a concise overview of the key requirements for each type of residency visa.

Application Process for Kuwait Residency Visas
Applying for a Kuwait residency visa involves a structured process that must be followed carefully to ensure approval. While specific details may vary by visa type, the general application process can be summarized in few key steps:
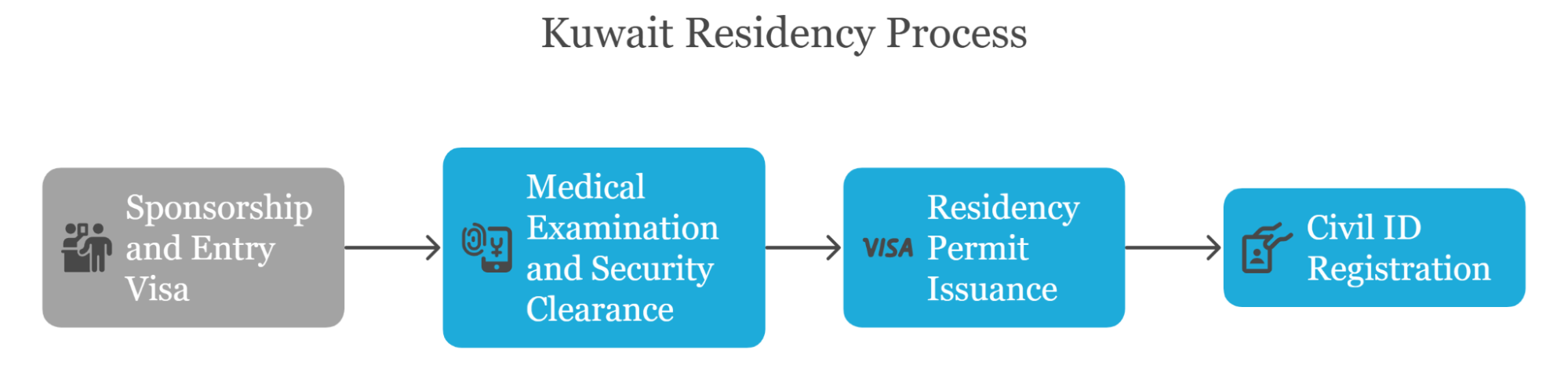
Step 1:Sponsorship and Entry Visa Issuance |
Step 2: Medical Examination and Security Clearance |
Step 3: Residency Permit Issuance |
Step 4: Civil ID Registration |
|
The process begins with a Kuwaiti sponsor—such as an employer, family member, or institution—submitting the necessary documents to the Ministry of Interior for initial approval. Once approved, the applicant is issued an entry visa, which allows them to legally enter Kuwait to complete the remaining residency formalities. |
After arrival, the applicant must undergo a medical examination at a government-approved health center. In addition, fingerprinting and a security background check must be completed with Kuwait’s relevant authorities to ensure public safety and compliance with residency regulations. |
Upon successful completion of medical and security procedures, the applicant is granted a residency permit. This may be issued as a visa sticker in the passport or as a digital entry linked to the Civil ID, depending on the latest regulations. |
The final step involves registering with the Public Authority for Civil Information (PACI) within 30 days of residency approval. The applicant must apply for a Civil ID card, which is mandatory for all legal, financial, and administrative transactions in Kuwait. |
Validity of Kuwait Residency Visas
The validity period of Kuwait residency visas depends on the visa type and the conditions set by the sponsor or relevant authority. Here's a breakdown of the general validity timelines:
|
Visa Type |
Validity |
|
Work Residency Visa (Article 18) |
Valid for 1–2 years, depending on the employer’s contract and permit duration. Renewable as long as employment continues. |
|
Family Residency Visa (Article 22) |
Typically valid for 1 year and renewable annually if the sponsor maintains valid residency and meets income requirements. |
|
Student Residency Visa |
Usually valid for the duration of the academic program (1–4 years). Must be renewed each academic year with proof of continued enrollment. |
|
Investor/Business Residency Visa |
Valid for 1–5 years, depending on the investment type and government approval. Generally renewable if business operations remain active. |
|
Domestic Worker Visa (Article 20) |
Typically valid for 1 year and renewable annually by the sponsoring employer. |
|
Temporary Residency Visa |
Valid for up to 3 months. Non-renewable and intended strictly for short-term stays. |
Processing Time and Fees for Kuwait Residency Visas
The processing time and associated fees for Kuwait residency visas vary depending on the visa type, applicant’s nationality, and the completeness of submitted documents. Here's a general overview:
Processing Time
The processing time for Kuwait residency visas depends on the visa type and the accuracy of submitted documents. Work and student visas typically take 2 to 4 weeks, while family visas may be processed in about 2 to 3 weeks.
Investor visas can take longer, up to 6 weeks, due to extra approvals. Domestic worker visas are generally faster, taking around 1 to 3 weeks, and temporary visas are usually issued within 1 to 2 weeks.
Fees
All residency visa types involve application and issuance fees, which vary based on the category. Additional charges may apply for medical exams, fingerprinting, and Civil ID registration.
Employers or sponsors may also incur administrative or sponsorship costs, especially in the case of work or domestic worker visas. Kuwait visa Fees are subject to change based on government policy and individual circumstances.
Residency Visa Renewal in Kuwait
Renewing a residency visa in Kuwait is a critical process to maintain legal residency status.
It is the responsibility of the sponsor—whether an employer, family member, or institution—to initiate the renewal application in a timely manner to avoid penalties or legal complications.
|
Category |
Detail |
|
Who Can Renew |
The sponsor (employer, family member, institution) or self (investors) |
|
When to Renew |
30–60 days before visa expiry to avoid fines or legal issues |
|
Where to Apply |
General Department of Residency Affairs or Ministry of Interior portal |
|
Required Documents |
- Valid passport - Current residency permit/Civil ID - Medical insurance (if applicable) - Sponsorship proof (e.g., work contract) - NOC (if required) |
|
Renewal Steps |
1. Sponsor submits application 2. Pay renewal fees 3. Update Civil ID through PACI after approval |
|
Tip |
Ensure dependent visas are renewed alongside the primary visa |
Why Choose Kuwait as Your Next Destination?

Kuwait is a popular destination for expatriates seeking new opportunities, particularly in the Middle East. Here are some of the key reasons why individuals and families choose to immigrate to Kuwait:
- Strong Job Market: Kuwait offers competitive salaries and tax-free income, especially in sectors like oil and gas, healthcare, education, construction, and finance. Professionals often find lucrative employment packages, including housing and travel allowances.
- High Standard of Living: Many expats enjoy a comfortable lifestyle in Kuwait, with access to modern infrastructure, international schools, quality healthcare, and numerous leisure facilities.
- Safety and Stability: Kuwait is considered one of the safest countries in the Gulf region, with low crime rates and strong public security. Political and economic stability also make it an attractive place for long-term residence.
- Cultural Diversity: Kuwait is home to a large expatriate population, creating a diverse and multicultural environment. English is widely spoken, and expats from various countries often find well-established communities and support networks.
- Business and Investment Opportunities: Entrepreneurs and investors benefit from strategic geographic positioning, growing market potential, and government initiatives aimed at encouraging foreign investment and private sector development.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, but you must get approval from both your current and new sponsor. The transfer is subject to Ministry of Interior approval and may depend on the visa type and how long you’ve worked with your current sponsor.
Overstaying your visa results in daily fines and could lead to legal issues, deportation, or future visa bans. It’s important to renew or cancel your visa on time.
Yes, if you meet the required income level, you can sponsor your immediate family under a family residency visa (Article 22).
Residents can generally stay outside Kuwait for up to six consecutive months. Exceeding this period may result in automatic cancellation of your residency unless you have prior approval.
No. Once a residency visa is canceled, it cannot be reinstated. A new visa must be applied for if the individual wishes to return to Kuwait.
Usually, a full medical exam is only required upon initial entry. Renewals typically don’t require a medical unless specifically requested by the authorities or for certain job categories.
Generally, no. Visit visas must be exited before applying for a residency visa. However, certain cases such as family reunification or special approvals may allow for in-country conversion.
Content Disclaimer: Although this information was last updated in June 2025, we recommend verifying with the appropriate agencies, embassies, and airlines to ensure complete accuracy regarding your travel plans.

To help us improve