
Working in Kuwait offers promising opportunities for professionals seeking employment in the Gulf region.
Known for its strong economy, tax-free income, and growing job market, Kuwait continues to attract skilled workers from around the world.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the Kuwait work visa, including eligibility requirements, application procedures, and other important considerations for those planning to live and work in the country. To start your employment journey smoothly, it is essential to apply for Kuwait Visa through the official channels and ensure all required documents are accurately submitted.
What is a Kuwait Work Visa?
A Kuwait Work Visa is an official authorization that allows foreign nationals to enter, live, and work legally in Kuwait under the sponsorship of a local employer. It is primarily issued for private sector employment and falls under Visa Article 18.
This visa is tied to a specific job offer, meaning the employer must initiate the application and act as your sponsor throughout your stay. Once the visa is granted, the holder is eligible to enter Kuwait, complete residency formalities, and begin working.
Key features of the Kuwait Work Visa include:
✓ Sponsored by a Kuwaiti employer
✓ Issued prior to arrival in Kuwait
✓ Linked to a specific job and employer
✓ Leads to residency status upon entry and completion of medical and security checks
Who Needs a Work Visa for Kuwait?
A work visa is required for all foreign nationals (except citizens of Gulf Cooperation Council countries) who wish to be employed in Kuwait. This applies to individuals seeking both skilled and unskilled jobs in the private or public sectors.
Individuals who need a Kuwait work visa include:
|
✓ Non-GCC nationals offered employment by a Kuwaiti company or institution ✓ Expatriates looking to relocate for work and residency in Kuwait ✓ Contract workers, consultants, or project-based hires working for extended periods ✓ New hires entering Kuwait for the first time under a job offer ✓ Workers transferring sponsorship to a new employer (in most cases, a new work visa is required) |
Exceptions
|
✓Citizens of GCC countries (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, Bahrain, and Oman) do not need a work visa but may still need to register for residency and employment purposes. |
Types of Work Visas in Kuwait
Kuwait primarily offers one main type of work visa for foreign nationals who wish to be employed in the country. This visa is structured to support private sector employment under the sponsorship of a licensed Kuwaiti employer.
1.Article 18 Visa – Private Sector Work Visa
This is the most common type of work visa in Kuwait. It allows foreign nationals to work for companies in the private sector. The visa is issued based on:
|
✓ A valid job offer from a Kuwaiti company ✓ Approval from the Ministry of Social Affairs and Labour ✓ Sponsorship by the employer, who is responsible for visa and residency processing |
2.Other Related Visa Categories (Not Direct Work Visas but Linked to Employment)
While Article 18 is the primary work visa, the following may relate to employment under specific conditions:
|
✓ Article 17 Visa – Public Sector Employment Visa: Issued to expatriates employed by government entities or public institutions. ✓ Project Visas: A subcategory of Article 18, granted to workers hired for government-awarded projects. These are employer-specific and usually non-transferable. ✓ Domestic Worker Visa (Article 20): Designed for individuals working as housemaids, drivers, or domestic staff. Sponsored directly by Kuwaiti households, not businesses. |
Requirements for a Kuwait Work Visa
To obtain a Kuwait work visa, both the employer and the employee must meet specific documentation and eligibility criteria. The process begins with the employer applying for a work permit, followed by the employee fulfilling all necessary conditions for visa approval.
General Requirements
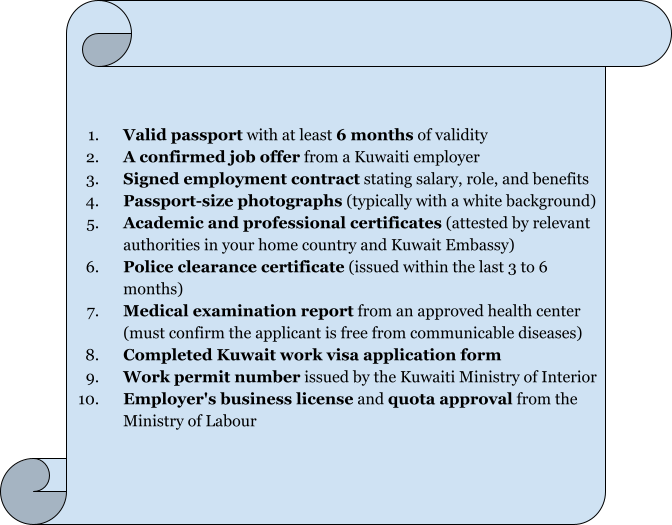
- Must be a registered company in Kuwait
- Must have visa quota approval from the Ministry of Social Affairs and Labour
- Must act as the official sponsor of the foreign worker
- Responsible for initiating the work permit request and submitting it to Kuwaiti authorities
- Must not have a criminal record
- Must meet qualification standards for the role being offered
- Must be in good health and pass all medical examinations
- Must provide attested academic and work documents as proof of eligibility
Application Process for a Kuwait Work Visa
Obtaining a Kuwait work visa is a structured process that must be initiated by a Kuwaiti employer. The visa allows the foreign national to legally enter and work in Kuwait under a sponsorship agreement. Below is are simple steps breakdown of the process:
1. Employer Applies for Work Permit
The employer submits a work permit request with required documents like the employee’s passport copy, job offer, and attested qualifications. Once approved, a visa reference number is sent to the Kuwaiti embassy in the worker’s country.
2. Employee Completes Embassy Process
The worker visits the Kuwaiti embassy, submits documents (passport, police clearance, medical report, etc.), and receives the entry visa to travel to Kuwait.
3. Arrival Formalities and Residency
After arriving, the employee completes a medical exam and fingerprinting. The employer then assists in getting the residency stamp and Civil ID, required for all legal activities in Kuwait.
Validity of a Kuwait Work Visa
A Kuwait work visa comes with specific validity terms that govern how long a foreign national can stay and work in the country. Understanding the visa’s initial validity, residency duration, and renewal rules is essential for both employees and employers.
-
Initial Visa Validity (Before Entry)
Once issued, the Kuwait work entry visa is typically valid for 90 days (3 months). This means the visa holder must enter Kuwait within this period; otherwise, the visa expires and a fresh application may be required.
-
Residency Validity (After Entry)
After the foreign worker arrives in Kuwait and completes the necessary medical tests, fingerprinting, and obtains the residency stamp, they are granted a residency permit (Iqama) under Article 18.
This residency is usually valid for 1 to 3 years, depending on the employment contract and employer’s sponsorship terms. It is renewable as long as the worker maintains legal employment and passes annual medical checks.
Processing Time and Fees for a Kuwait Work Visa
Understanding the estimated timelines and the types of fees involved can help applicants and employers prepare accordingly.
While the process is generally straightforward, delays may occur if documentation is incomplete or additional verification is required.
Processing Time
The full process typically takes several weeks and includes the following stages:
- Work Permit Approval: Once the employer submits all required documents, the Ministry of Social Affairs and Labour generally processes the permit within 1 to 3 weeks.
- Visa Issuance at Embassy/Consulate: After the permit is approved and the visa reference number is issued, the applicant must visit the Kuwaiti diplomatic mission in their home country. The visa stamping process usually takes 1 to 2 weeks, depending on document verification and embassy workload.
- Post-Arrival Formalities: Upon entering Kuwait, the applicant must undergo a medical exam, biometric registration (fingerprinting), and apply for a residency permit and civil ID. These steps are typically completed within 1 to 2 weeks.
Estimated total time from employer application to full legal residency:approximately 4 to 8 weeks, though timelines can vary by case.
Fees
The Kuwait work visa process involves several official fees at different stages. These may include:
|
✓ Work permit issuance ✓ Visa stamping by the Kuwaiti embassy or consulate ✓ Medical testing and fingerprinting upon arrival ✓ Residency stamping and civil ID issuance |
The exact fee amounts are subject to change and can vary based on the applicant’s nationality, job classification, and contract terms. In many cases, employers cover the associated costs, but this should be clarified in advance.
Can You Bring Your Family on a Kuwait Work Visa?

Yes, foreign nationals holding a valid Kuwait work visa (Article 18) may sponsor their immediate family members, such as a spouse and children, through a dependent (family) visa, subject to meeting the eligibility criteria established by Kuwaiti immigration authorities.
Sponsorship Eligibility
To sponsor dependents, the primary visa holder must:
|
✓ Possess a valid residency permit under Article 18 ✓ Demonstrate the financial ability to support family members ✓ Maintain legal residency status in Kuwait ✓ Provide adequate accommodation within the country |
Family Members Eligible for Sponsorship
The following individuals are typically eligible for dependent visas:
✓ Spouse
✓ Children, generally minors (special provisions may apply in certain cases)
The sponsoring worker must submit an application to the Ministry of Interior, supported by:
|
✓ Valid passport copies of the sponsor and dependents ✓ Marriage certificate and/or birth certificates, properly attested ✓ A valid civil ID and residency proof ✓ Documentation showing employment and housing arrangements |
Note: Parents, siblings, or extended family members are not eligible under this visa category, except in rare cases, subject to official approval based on humanitarian grounds.
Tips for a Successful Kuwait Work Visa Application
Applying for a Kuwait work visa requires careful attention to detail and compliance with immigration procedures. To increase your chances of approval and avoid unnecessary delays, consider the following tips:
- Ensure your employer is legally registered: Your sponsor must be an authorized and licensed Kuwaiti company approved to hire foreign workers.
- Provide accurate and complete documentation: Submit a valid passport, attested educational and professional certificates, and any additional documents required by Kuwaiti authorities.
- Comply with embassy or consulate requirements: Follow instructions from the Kuwaiti embassy in your home country carefully, especially regarding appointments, medical tests, and document verification.
- Stay updated on visa and immigration policies: Rules and procedures may change. Monitor updates from the Kuwait Ministry of Interior or consult your employer for current requirements.
- Maintain regular communication with your employer: Stay in touch with your sponsor to ensure they complete their part of the application promptly and assist you throughout the process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Processing time typically ranges from 9-12 Working Days, depending on how quickly documents are submitted and verified by both the employer and Kuwaiti authorities.
Yes, but changing employers requires formal approval from the Ministry of Interior. The new employer must apply for a visa transfer, and conditions may apply based on your current contract.
Yes. A medical examination is mandatory and usually includes blood tests, chest X-ray, and screening for infectious diseases. You must also pass a medical check upon arrival in Kuwait.
Yes. You may sponsor your spouse and children under a dependent visa, provided you meet the eligibility requirements and have legal residency in Kuwait.
Yes. Once you are issued a residency permit, it is generally valid for 1 to 3 years and can be renewed by your employer before it expires.
Yes, as long as your residency permit is valid, you may leave and re-enter Kuwait. Be sure to carry your civil ID and ensure your travel does not conflict with any work obligations.
If rejected, you should consult your employer or sponsor for clarification. You may reapply after addressing the reasons for rejection, which could include incomplete documentation or ineligibility.
Content Disclaimer: Although this information was last updated in June 2025, we recommend verifying with the appropriate agencies, embassies, and airlines to ensure complete accuracy regarding your travel plans.

To help us improve